Current Projects
Geometric computing for integrated circuit design
Geometric computing for integrated circuit design
Industrial contract between ANSYS Hellas, and ATHENA RC.
Nov. 2020 — today
Geometric data structures, 3d medial axes/surfaces, and random walks for uniform sampling are essential and standard tools in the evaluation of circuit designs. The project upgrades and enhances such approaches with novel methods that leverage parallel or distributed computing, trade-offs between speed and exactness, data-driven algorithm design, and machine learning.
Google Summer of Code
Our students have benefited from a few GSoC fellowships

Past Projects
AutoFair: Removing bias from ML
Duration: 3 yrs starting on October 1st, 2022
Framework: Horizon Europe
Partners: Czech Technical University (Coord.), Athena RC, NKUA, Imperial College London, Technion, Workable, etc
AutoFair aims at algorithmic methods for removing bias from ML pipelines, and at enhancing explainability of AI models, focusing on 3 use cases. The first is the automation of fair evaluation in recruitment, the second is the elimination of gender inequality in advertising and the third is the area of fin-tech, specifically the elimination of discrimination against bank clients.
DT4GS: Digital twins for green shipping
Duration: 3 yrs starting in Spring 2022
Framework: Horizon Europe
Partners: Inlecom Systems (Belgium, Coord.), Athena, and another 19 entities.
DT4GS is aimed at delivering an “Open Digital Twin Framework” for both shipping companies and the broader waterborne industry actors to tap into new opportunities made available through the use of Digital Twins(DTs). The project will enable shipping stakeholders to embrace the full spectrum of DT innovations to support smart green shipping in the upgrade of existing ships and new vessels. DT4GS will cover the full ship lifecycle by embracing federation of DT applications as well as utilising DTLF policies and related shared-dataspace developments for the sector. DT4GS applications will focus on shipping companies but will also provide decarbonisation decision-support system for shipyards, equipment manufacturers, port authorities and operators, river commissions, classification societies, energy companies and transport/corridor infrastructure companies. DT4GS’s objectives are to:
- Support shipping companies in achieving up to 20% reduction in CO2e with a 2026 horizon, by developing and deploying real-time configurable DTs for ship and fleet operational performance optimisation in 4 Living Labs involving shipping companies, with different vessel types, and establishing fully validated industry services for Green Shipping Operational Optimisation DTs expected to be adopted by 1000+ ships by 2030.
- Establish a comprehensive zero-emission shipping methodology and support Virtual Testbed and Decision Support Systems that address both new builds and retrofits comprising: (a) A DT4GS (Green Shipping) Dataspace for the broader shipping sector contributing to GAIA-X by establishing a core European industry resource that accelerates the green and digital transition of waterborne shipping and transport value chains. (b) Simulation based solutions to retrofit ships, targeting 55% reduced CO2e reduction by 2030. (c) A smart green “new-build” reference design per vessel type. (d) Virtual Testbed services for reducing the cost of physical testing of GS solutions by 20%.
RANWALK: Random walks for integrated circuit design
Duration: 30 months starting in Spring 2022
Framework: Research-Innovate-Create (Greek Ministry of Development)
Partners: HELIC / ANSYS Hellas (coord.), U Patras, Athena RC.
Random Walk for Fast, Geometry-Agnostic IC Modelling
The sector of design tools for Integrated Circuits (ICs) is a critical link of the Semiconductor industry. Recently, a new segment has been emerging in the EDA market, to cover new needs for the detection and avoidance of electromagnetic Crosstalk noise, in the high value and fast-growing markets of high-performance Digital ICs (e.g. GPU, CPU), memories and heterogeneous Systems in Package (SiP). The main proposed research axes are: (1) Development of a Random Walk algorithm for parasitic capacitance extraction (2) Computation Geometry methods with emphasis in the efficient solution of the Maximum Empty Cube problem (3) Optimisation of the modelling engine via pre-characterisation of Green functions used for sampling.
Μέθοδος Τυχαίων Περιπάτων για Ταχεία, Γεωμετρικά Αγνωστικιστική Μοντελοποίηση Ολοκληρωμένων Κυκλωμάτων
Ο κλάδος των σχεδιαστικών εργαλείων για ολοκληρωμένα κυκλώματα (Electronic Design Automation) είναι εξαιρετικά κρίσιμος κρίκος της αλυσίδας αξίας του τομέα των Ημιαγωγών. Σήμερα, έχει δημιουργηθεί πρακτικά ένα νέο τμήμα στην αγορά EDA, για την κάλυψη των νέων αναγκών εντοπισμού και αποφυγής ηλεκτρομαγνητικού θορύβου τύπου Crosstalk, στις μεγάλες αγορές των ψηφιακών κυκλωμάτων υψηλών προδιαγραφών (π.χ. GPUs, CPUs), των μνημών και των ετερογενών, εντός κοινής συσκευασίας συστημάτων (Systems in Package). Οι βασικοί άξονες έρευνας που θα πλαισιώσουν την προτεινόμενη μηχανή μοντελοποίησης είναι: (1) Ανάπτυξη αλγορίθμου Random Walk για την εξαγωγή χωρητικοτήτων. (2) Ανάπτυξη μεθόδων Υπολογιστικής Γεωμετρίας με έμφαση στον αποτελεσματική υπολογισμού του μέγιστου κενού κύβου. (3) Βελτιστοποίηση της μηχανής μοντελοποίησης μέσω προ-χαρακτηρισμένων συναρτήσεων δειγματοληψίας.
GRAPES: learning, processing and optimizing complex shapes
Marie Sklodowska-Curie European Training Network (H2020)
Dec 2019 — Nov 2023.
Members:
ATHENA Research Center (coordinator),
U. Barcelona (Spain), INRIA (France), J. Kepler U. Linz (Austria), RWTH Aachen (DE), SINTEF (Norway), U. Svizzera Italiana (CH), U. Strathclyde (UK), U. Tor Vergata Roma (IT), U. Vilnius (LI), GeometryFactory Sarl (FR).
GRAPES aspires to promote game changing approaches for generating, optimising, and learning 3D shapes by leveraging progress in Computational Mathematics, Numerical Analysis, and Algorithm Design, up to Geometric Modelling, Shape Optimisation, and Deep Learning. Innovation is at the core of our work and relies on the active participation of SMEs, either as a beneficiary hosting an ESR or as associate partners hosting secondments. Concrete applications include simulation and fabrication, hydrodynamics and marine design, manufacturing and urban planning, reconstruction and visualisation, retrieval and mining. Research is articulated in 3 workpackages: Shape processing and geometric computing, Shape optimization and isogeometry, and Machine learning of shapes, including geometric deep learning.
FinAI
Fintech and Artificial Intelligence in Finance
Cost Network. 2020 — 2023.
The Project investigates AI and Fintech with respect to: Transparency, Black Box Decision-Support Models in the Financial industry, and Investment Product Performance for clients.
National Research Infrastructures on Integrated Structural Biology, Drug Screening, and Drug Target functional characterisation
EPAnEK 2014-2020 Operational Programme: Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship, Innovation
Jan. 2019 — Dec. 2021.
INSPIRED aims to address the needs of the scientific community in Structural Biology and the broader Biosciences, aiming at the identification and study of new biomolecules and bioactive compounds and their Pharmacological evaluation. The integration of Structural Biology combining Molecular Cellular and Genomics promotes research at the regional level, trains new scientists, and offers services to users of the South East Mediterranean, underlining how the geopolitical position of Greece promotes the objectives of the Infrastructure. NKUA/Erga participates in Project 5 by using Structural Bioinformatics and Machine Learning for modelling and analysing macromolecules and systems. For details visit the Lab’s webpage on bioinformatics.

Lambda: Learning and Analysing Massive / Big complex Data
Marie Sklodowska-Curie Reasearch-Innovation Staff Exchange
March 2017 — August 2022.
Members: NKU Athens (coordinator), 3D Industries (London), AXA GIE (Paris).
LAMBDA aims at transferring game changing technologies to the European industry in critical areas of Machine learning. It focuses on two distinct application domains: 3D shape analysis and unstructured data mining. Both tasks are organised around representative companies in the respective domains. Besides inter-sectoral collaborations, we exploit the international dimension by associating leading USA Universities (Stanford, U. Illinois Chicago, UC Berkeley), so as to bring state-of-the-art methods developed at the global level into the European framework.

ΠήΓΑΣΟΣ / Geometric approximation algorithms & applications to fintech
Young Researchers (Ministry of education)
Mar. 2020 — June 2021.
Funding: 2 PhD students at ATHENA Research Center.
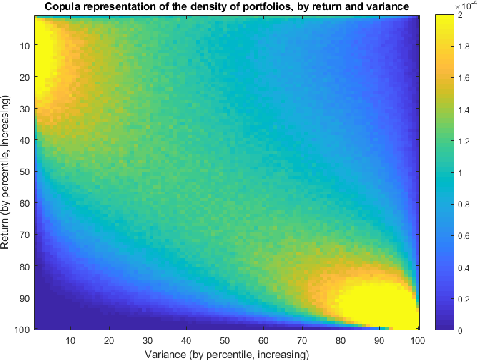
Geometric computations of scale allow us to model portfolios and their distribution so as to eventually model the cross-sectional behaviour of entire market — typically the stock market but the approach extends to other markets too. We develop efficient sampling, random walks, and volume approximation to compute the copula (figure), that is the joint distribution of revenue and volatility for a set of portfolios of fixed investment. Machine learning techniques on these distributions should give an indicator of the state of the market, distinguishing between normal times, bubbles and crises. Our tools serve to evaluate portfolios but also to identify or even predict market crises.
ARCADES
Algebraic Representations in Computer-Aided Design for complEx Shapes
Marie Sklodowska-Curie European Training Network, Jan 2016 — Dec 2019.
Members: ATHENA Research Center (coordinator), U. Barcelona (Spain), INRIA (France), J. Kepler U. Linz (Austria), SINTEF (Norway), U. Strathclyde (UK), T.U. Wien (Austria), Evolute GmbH (Austria).
ARCADES aims at disrupting the traditional paradigm in Computer-Aided Design (CAD) by exploiting cutting-edge research in mathematics and algorithm design. Geometry is now a critical tool in a large number of key applications; somewhat surprisingly, however, several approaches of the CAD industry are outdated, and 3D geometry processing is becoming increasingly the weak link. This is alarming in sectors where CAD faces new challenges arising from fast point acquisition, big data, and mobile computing, but also in robotics, simulation, animation, fabrication and manufacturing where CAD strives to address crucial societal and market needs. The challenge taken up by ARCADES is to invert the trend of CAD industry lagging behind mathematical breakthroughs and to build the next generation of CAD software based on strong foundations from algebraic geometry, differential geometry, scientific computing, and algorithm design. Our game-changing methods lead to real-time modelers for architectural geometry and visualisation, to isogeometric and design-through-analysis software for shape optimisation, and marine design & hydrodynamics, and to tools for motion design, robot kinematics, path planning, and control of machining tools. Here is a video of work on simplifying models by A. Fuentes.

CloudFlow
Electronics design automation on the Cloud
I4MS: Innovation for Manufacturing SMEs, February 2015 — January 2016.
Members: Helic S.A. (Leader), ATHENA Research Center, European Sensor Systems (ESS), Arctur racunalniški inženirin (Slovenia).
We, at ATHENA, optimize the geometric modeling tools of HELIC, especially in what concerns scientific computing for grid usage and the cloud provided by Arctur. ESS, MEMS sensors producer, will use modeling and simulation tools by HELIC to investigate for possible detrimental self- and mutual- inductance effects on their sensor front-end designs, option previously not available due to high cost of modeling software.

ESPRESSO
Exploiting Structure in Polynomial Equation and System Solving for geOmetric and game mOdeling.
Excellence Programme, EU and Ministry of Development. October 2012 — September 2015.
ESPRESSO members: I. Emiris (PI), Y. Avrithis and R. Vidunas (Postdocs), A. Karasoulou (PhD student), E. Koutsoupias (U. Athens, U. Oxford), B. Mourrain (INRIA), P. Bro Miltersen (U. Aarhus).
The complexity of polynomial equation and system solving is often too high, hence the need for algorithms that exploit the structure of the problem, leading to complexity bounds in terms of its intrinsic rather than nominal hardness. Structure is multifarious: We consider the sparseness of the input, and reducing the problem to methods that operate on sparse objects. ESPRESSO focuses on two specific applications. The first is geometric modeling, where we have extensive experience and expect to obtain tangible and practical results, based on effective, publicly available implementations. Our second application uses algebraic tools to better model stochastic games with the goal of effectively computing finite or infinite game equilibria. Further info.

ΘΑΛΗΣ: Geometric Computing (GeomComp)
Advanced Geometric Computing and Critical Applications (website)
January 2012 — September 2015. Ministry of Education and EU (acks). Budget: 520,000 euro.
GeomComp includes 3 Greek teams, namely:
- ErGA (coordinating), Dept Informatics & Telecoms, University of Athens. Faculty members: Ioannis Emiris (team leader), Dimitrios Gunopulos. The group includes Leonidas Palios (University of Ioannina), Euripides Markou (University of Thessaly).
- School of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, National Technical University of Athens. Faculty members: Panagiotis Kaklis (team leader), Alexandros Ginnis.
- Foundation for Research and Technology – Hellas (FORTH), Heraklio, Crete. Faculty members: Menelaos Karavelas (team leader), Vassilis Samoladas (Technical U. Crete).
GeomComp involves external partners, who include L. Guibas (Stanford University, USA) and E. Papadopoulou (U. Svizzera Italiana, Lugano, Switzerland).
The main topics include (details in Greek):
- Computational geometry and generalizations: convex geometry with extensions to higher dimensions and nonlinear objects, Voronoi diagrams in 2D with extensions to 3D and curved objects, visibility with linear obstacles with extensions to nonlinear obstacles, nearest-neighbor queries with extensions to data-mining, approximate geometric optimization with extensions to massive data.
- Nonlinear computational geometry, Computer-aided geometric design, and Geometric modeling, including the development of the required mathematical tools.
- Software development and applications to critical questions in structural bioinformatics, molecular modeling, and industrial design, such as VLSI and ship design.

CG Learning: Computational Geometry Learning
European FET-Open STREP project, November 2010 — October 2013.
It includes 7 Universities and one Research Institute.
The tasks of ErGA are: High-dimensional polytopes, silhouettes and projections. General-dimensional kernel for CGAL and the Orientation predicate. Approximate nearest neighbor search and the related data structures.
SAGA: ShApes, Geometry and Algebra
European Marie Curie Initial Training Network (FP7).
November 2008 — October 2012.
It includes 5 Universities, 3 Research Institutes, and 2 Companies, and its aim is to advance the mathematical and algorithmic foundations of CAD technology, by exploiting results and techniques from different fields, such as Computer Algebra, Algebraic Geometry, Numeric Computation, and Theory of Algorithms. The ErGA PhD fellow is Tatjana Kalinka, the postdoc fellow is Thang Luu Ba, and PhD student Angelos Mantzaflaris has visited ErGA from INRIA Sophia-Antipolis.
There are SAGA training events, open to participants outside the Network: November 2008, in Castro Urdiales, Spain. March 2010 in Auron, France. October 2010 in Kolympari, Greece. September 2011 at Vilnius, Lithuania. October 2012 at Trento, Italy.

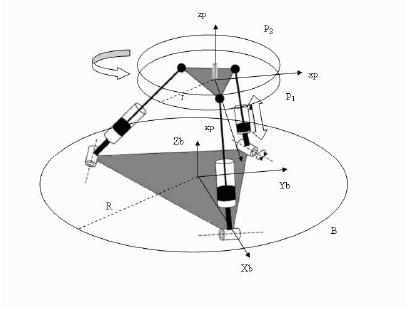
Algorithms for robotic platforms in physiotherapy
Project ΠΕΝΕΔ, “Algorithm design and software development for parallel robotic mechanisms and applications to physiotherapy”, 1/7/05 – 31/12/10.
Joint funding by Ministry of Development, and “Reflexion Ltd”.
PhD students: Christos Konaxis, Christos Sirseloudis, and Elias Tsigaridas. Engineer: Artemis Maglara. Collaboration with Instituto de Automatica Industrial (Madrid), INRIA (Sophia-Antipolis), Institute of Computer Science (FORTH, Heraklio).
The aim of the project is to study and design a robotic platform for the rehabilitation of patients with kinetic problems and with posible remote control capabilities. For this purpose the kinematics of the foot are extensively studied and useful results are extracted such as the foot axes of rotaion, workspace, velocities, accelerations and forces that must be handled by a robotic device. Identification / calibration techniques are also studied in order to compute the specific kinematics parameters of the patient’s foot. A new hybrid parallel / serial robotic platform is proposed and its parametric design is carried out in order to follow the foot movemets. Ancillary algebraic and numeric algorithms are developed.
ACS: Algorithms for Complex Shapes
IST-STREP (Open FET) FP6 project (greek/english summary) 1/5/05-30/4/08. Arrangements, Voronoi diagrams of ellipses (PhD by G.Tzoumas), visibility in curved art galleries, CGAL algebraic kernel, operations on complex shapes, predicates’ implementation, algebraic benchmarking, CGAL-Python.
Figure by T. Kakargias, using a map from the Cartography Laboratory, NTUA.

Αlgorithms for curves and surfaces
Efficient algorithms and implementations for the representation and manipulation of curves and surfaces. Project ENTER, Greek Ministry of Development. Visitor scientist: Ilias Kotsireas (W. Laurier Univ., Waterloo, Canada). Collaboration with company “MP & Associates”. 2006-08.
CALAMATA
Team association (Equipe Associe’e) with the GALAAD Group of INRIA Sophia-Antipolis, France, 1/03-12/07.
PLATON project
Calibration of Parallel platforms and applications in space robots. Bilateral PLATON project with the COPRIN Group of INRIA Sophia-Antipolis, France, 1/04-8/06.